Page 29 - AWA-41-No.1 issue
P. 29
INDIA AGRICULTURE ExPORT
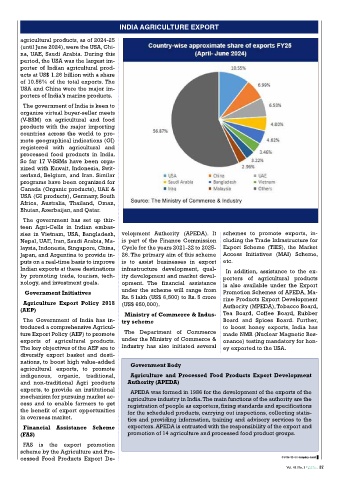
agricultural products, as of 2024-25
(until June 2024), were the USA, Chi-
na, UAE, Saudi Arabia. During this
period, the USA was the largest im-
porter of Indian agricultural prod-
ucts at US$ 1.26 billion with a share
of 10.55% of the total exports. The
USA and China were the major im-
porters of India’s marine products.
The government of India is keen to
organize virtual buyer-seller meets
(V-BSM) on agricultural and food
products with the major importing
countries across the world to pro-
mote geographical indications (GI)
registered with agricultural and
processed food products in India.
So far 17 V-BSMs have been orga-
nized with Kuwait, Indonesia, Swit-
zerland, Belgium, and Iran. Similar
programs have been organized for
Canada (Organic products), UAE &
USA (GI products), Germany, South
Africa, Australia, Thailand, Oman,
Bhutan, Azerbaijan, and Qatar.
The government has set up thir-
teen Agri-Cells in Indian embas-
sies in Vietnam, USA, Bangladesh, velopment Authority (APEDA). It schemes to promote exports, in-
Nepal, UAE, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Ma- is part of the Finance Commission cluding the Trade Infrastructure for
laysia, Indonesia, Singapore, China, Cycle for the years 2021-22 to 2025- Export Scheme (TIES), the Market
Japan, and Argentina to provide in- 26. The primary aim of this scheme Access Initiatives (MAI) Scheme,
puts on a real-time basis to improve is to assist businesses in export etc.
Indian exports at these destinations infrastructure development, qual- In addition, assistance to the ex-
by promoting trade, tourism, tech- ity development and market devel- porters of agricultural products
nology, and investment goals. opment. The financial assistance is also available under the Export
Government Initiatives under the scheme will range from Promotion Schemes of APEDA, Ma-
Rs. 5 lakh (US$ 6,500) to Rs. 5 crore rine Products Export Development
Agriculture Export Policy 2018 (US$ 650,000). Authority (MPEDA), Tobacco Board,
(AEP)
Ministry of Commerce & Indus- Tea Board, Coffee Board, Rubber
The Government of India has in- try scheme Board and Spices Board. Further,
troduced a comprehensive Agricul- to boost honey exports, India has
ture Export Policy (AEP) to promote The Department of Commerce made NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Res-
exports of agricultural products. under the Ministry of Commerce & onance) testing mandatory for hon-
The key objectives of the AEP are to Industry has also initiated several ey exported to the USA.
diversify export basket and desti-
nations, to boost high value-added Government Body
agricultural exports, to promote
indigenous, organic, traditional, Agriculture and Processed Food Products Export Development
and non-traditional Agri products Authority (APEDA)
exports, to provide an institutional APEDA was formed in 1986 for the development of the exports of the
mechanism for pursuing market ac- agriculture industry in India. The main functions of the authority are the
cess and to enable farmers to get registration of people as exporters, fixing standards and specifications
the benefit of export opportunities for the scheduled products, carrying out inspections, collecting statis-
in overseas market. tics and providing information, training and advisory services to the
Financial Assistance Scheme exporters. APEDA is entrusted with the responsibility of the export and
(FAS) promotion of 14 agriculture and processed food product groups.
FAS is the export promotion
scheme by the Agriculture and Pro-
cessed Food Products Export De- Circle 35 on enquiry card
Vol. 41 No. 1 27